Physical medicine
Acupressure as a Model for Complementary and Alternative Medicine (CAM) Treatment Following Acquired Brain Injury: Translating Lessons from the Laboratory
Acquired brain injury (e.g., stroke and traumatic brain injury or TBI) and associated sequelae are highly prevalent in the United States (U.S.), impacting both civilians and military populations. Because conventional treatments can be limited and functional recovery incomplete, complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) is often sought out.

The popularity of CAM exists despite inconclusive research findings for CAM treatments for injuryassociated sequelae. Apparent methodological limitations in CAM studies include issues related to experimental design, control groups, sample size, blinding and disparities in outcome measures. Overcoming these limitations poses challenges, but not insurmountable ones.
Instrumental Assessment of Balance Functional Performance. A Numerical Score to Discriminate Defective Subjects: A Retrospective Study
Balance keeping is a key functional performance that becomes of crucial importance with increasing age when frailty makes falling a traumatic event. This functionality can be measured through several tests such as the Instrumented Romberg Test on a Force Platform. Many parameters and indicators obtained through this test have been proposed to quantify performance deficit and to point to possible aetiological causes. However, in spite of many studies, no final definition has been agreed upon.
Rather, it seems that different combinations of strategies – probably in connection with anthropometrics, personal attitudes and lifestyle – can effectively solve the biomechanical problem of balance keeping. Such variability, in turn, entails a wide range of variability of all the individual parameters used to describe the path followed by the Center of Pressure over the force platform surface during the test. Ultimately, such a wide range makes the classical parameters rather undependable, when considered one by one, for clinical diagnostics.
Peripheral Muscle Dysfunction in Interstitial Lung Disease: A Scoping Study
A scoping study was performed by searching multiple electronic databases for published papers and conference abstracts of any study design that included a measure of peripheral muscle dysfunction and/or structural and metabolic characteristics of muscle. All sub-types of ILD were eligible. Forty-five studies representing 2522 individuals with 34 sub-types of ILD were included in this study. Data were charted using descriptive numerical analysis of study characteristics.
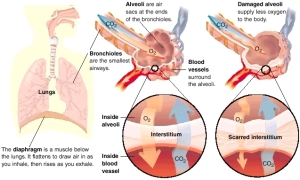
Peripheral muscle dysfunction was predominantly reflected by reduced volitional isometric strength (17 studies), whereas the evaluation of muscle endurance was rare (2 studies). Volitional muscle force or torque was measured in the quadriceps (14 studies) and handgrip (8 studies), with strength preferentially reduced in the lower limbs. Eight studies measured structural or metabolic characteristics and found evidence of reduced muscle size and oxidative stress. Findings of muscle injury and muscle inflammation (e.g. serum markers, electromyography and muscle biopsies) were reported primarily in individuals with idiopathic inflammatory myopathies and connective tissue diseases.
Deep Oscillation Therapy to treat Lymphederma cases
Lymphederma is a medical condition of fluid retention locally leading to swelling, pain and bruises. Deep oscillation therapy (DOT offers pain relief and reduce the swelling in the affected areas to the patients that is suffering from Lymphederma.
Vibration technology is used to apply intermittent electrostatic charges deep into the tissues. This would provide cyclic movement of the tissue so that the fluid would be pumped in. This therapy would not only help in healing the wound, but also helpful in curing fibromyalgia syndrome